Sjögren's Syndrome
OVERVIEW
Sjögren's syndrome is an autoimmune disease characterized by exocrine gland lymphocytic infiltration, which can be associated with neurologic, vascular, and other manifestations.
There are 2 Sjögren’s syndrome subcategories:1
- Primary Sjögren’s syndrome: occurs in isolation
- Secondary Sjögren’s syndrome: occurs in association with other connective tissue diseases (CTD)
- Most commonly:
- Rheumatoid arthritis (RA)
- Systemic lupus erythematous (SLE)
- Systemic sclerosis (SSc)
- Most commonly:
EPIDEMIOLOGY
In the United States, approximately 1-4 million people are living with Sjögren’s syndrome. Onset of disease typically occurs in individuals over 40 years of age.2
RISK FACTORS
- Women are more likely to develop the disease than men2
- Genetic predisposition:
- Family history of autoimmune diseases3
- HLA class II haplotypes human leukocyte antigen-DR (HLA-DR) and human leukocyte antigen-DQ (HLA-DQ)3
New insights in Sjögren’s syndrome pathogenesis suggest the disease occurs in individuals who have a genetic predisposition subsequent to exposure to an environmental trigger (hypothesized to be a viral trigger).3
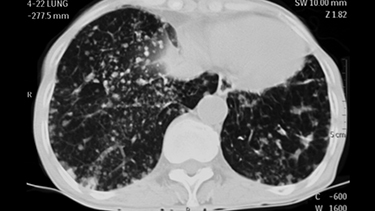
SJÖGREN’S SYNDROME-ILD: EPIDEMIOLOGY5
- Approximately 25% of patients with Sjögren’s syndrome develop interstitial lung disease (ILD)
- ILD tends to be mild and self-limited